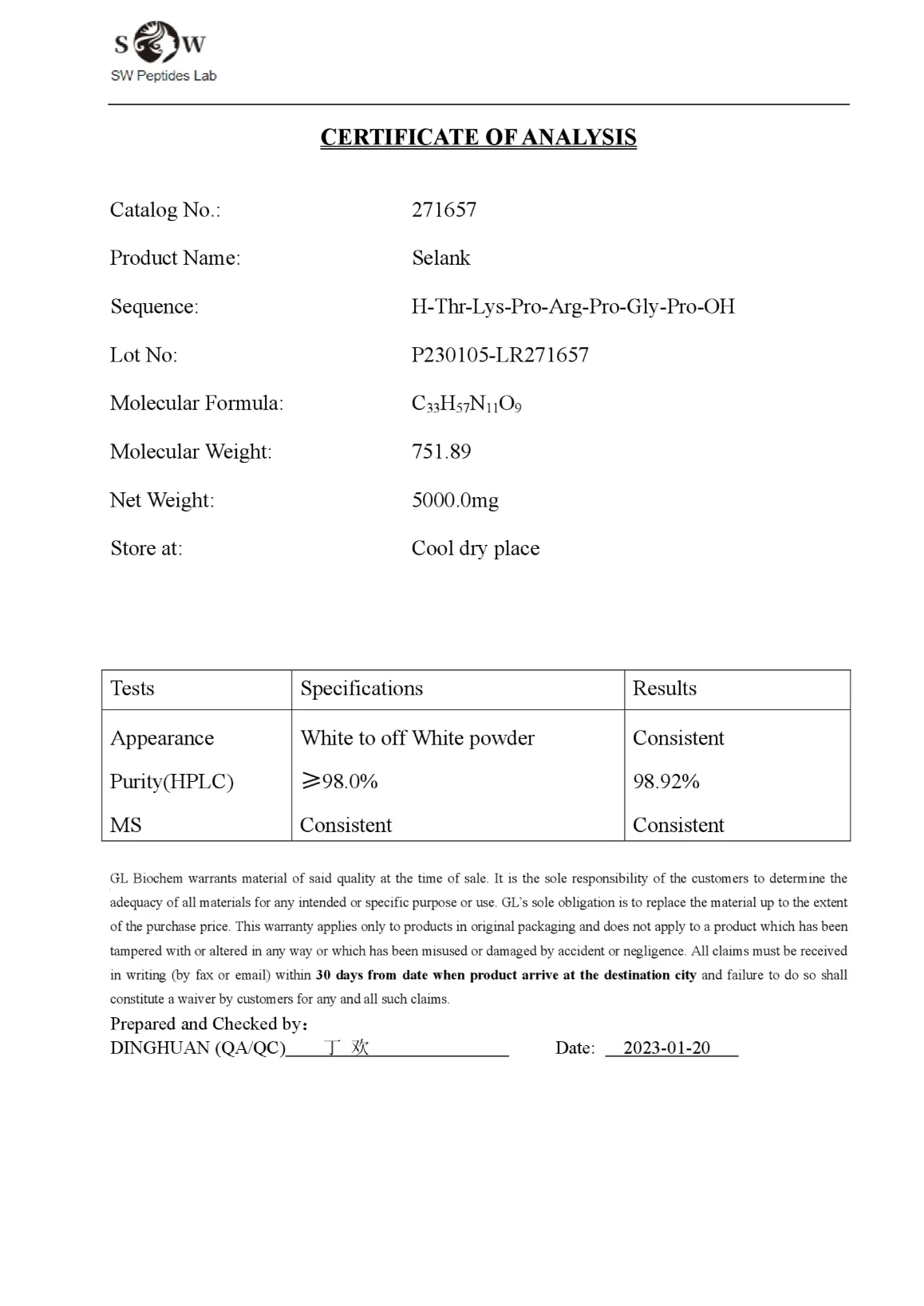
Selank 5mg
$17.50 - $26.00
You save
- Physical profile: Lyophilized powder
- This product is sold as a research chemical and not for human or animal consumption. For laboratory use by qualified professionals.
Availability: Ships today if ordered and paid by 12 PM EST. (Except Saturdays & Sundays)
Product Usage
This PRODUCT IS INTENDED AS A RESEARCH CHEMICAL ONLY. This designation allows the use of research chemicals strictly for in vitro testing and laboratory experimentation only. All product information available on this website is for educational purposes only. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law. This product should only be handled by licensed, qualified professionals. This product is not a drug, food, or cosmetic and may not be misbranded, misused or mislabled as a drug, food or cosmetic.
What is Selank/Semax? Help people who have Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) and Parkinson’s Disease (PD)Both Selank and Semax are melanocortins and have pleiotropic effects involved in brain health and function. Selank by itself has traditionally been prescribed for anxiety and depression.
Protocol
Clinical Research